Capture Wide Spectrum of Sunlight for Hydrogen Production
Au@Cu7S4 Yolk@Shell Nanocrystals Set New Hydrogen Production Activity Record under Visible and Near Infrared Irradiation
Tags: Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan, Energy & Environment, Science & Exploration
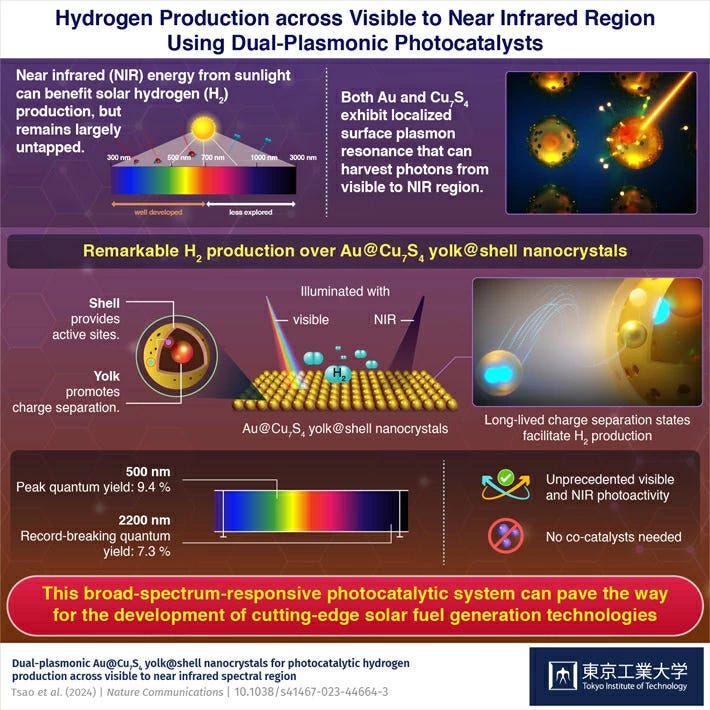
Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology and National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University have developed a novel Au@Cu7S4 yolk@shell photocatalyst that harnesses both visible and near-infrared light, significantly enhancing solar hydrogen production. This innovation addresses the challenge of capturing the wide spectrum of sunlight, particularly the near-infrared wavelengths that many current technologies fail to utilize. The Au@Cu7S4 photocatalyst achieves exceptional quantum yields in hydrogen production without the need for additional co-catalysts. Its dual-plasmonic optical properties optimize energy conversion, offering a potent solution for sustainable solar fuel generation. This technology is poised to reduce dependence on non-renewable energy sources, supporting a shift towards green energy applications.
IP Type or Form Factor: Material; Platform
TRL: 5 - prototype ready for testing in intended environment
Industry or Tech Area: Hydrogen Energy; Nanotechnology