Low-Cost, High-Surface Graphene Foam Boosts Energy Storage
Synthesis of Graphene Foam with Controllable Pore Sizes
Tags: National University of Singapore, Singapore, Energy & Environment, Science & Exploration
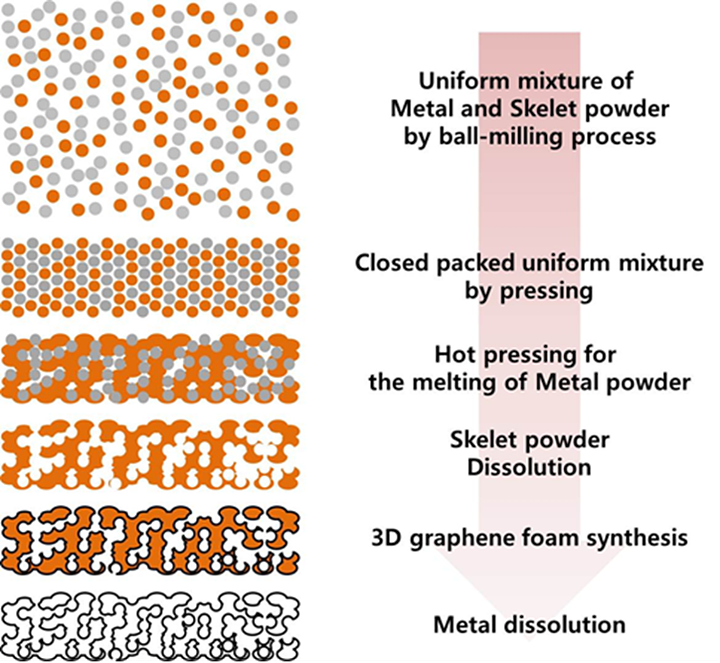
This innovation introduces a cost-effective method for synthesizing 3D graphene foam with controlled pore sizes, enhancing its suitability for energy storage applications. With pore sizes of 5 nm or less, the graphene foam achieves high surface area and electrical conductivity, making it ideal as an electrode material for batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells. The process involves layering graphene sheets around a skelet powder and removing the powder, resulting in a highly crystalline and porous foam. By controlling pore density and surface area, this method improves electrode efficiency and supports commercial-scale graphene foam production. Applications span energy storage and fuel cell systems, with significant potential across the energy and electronics industries.
IP Type or Form Factor: Material; Process & Method
TRL: 4 - minimum viable product built in lab
Industry or Tech Area: Battery Storage & Portable Power; Nanotechnology